AI coding assistant FAQs addressed in this article:
-
What are AI Coding Assistants? – AI Coding Assistants are tools designed to automate coding tasks, suggest improvements, and help developers write code more efficiently and accurately.
-
How do AI Coding Assistants transform software development? – They streamline workflows, improve code quality, and accelerate development cycles, enabling developers to focus on innovation and complex problem-solving.
-
What makes Cprime’s CodeBoost™ unique among AI Coding Assistants? – CodeBoost™ offers customization, seamless integration with existing tech stacks, and comprehensive support, making it a holistic solution for software development.
-
Why is a strategic approach important for integrating AI Coding Assistants? – A strategic approach ensures AI tools are effectively utilized, aligned with business goals, and integrated into workflows for maximum impact and competitive advantage.
-
How do AI Coding Assistants empower developers? – By automating routine tasks and offering code suggestions, AI Coding Assistants free developers to focus on creative problem-solving and innovation.
-
What future developments can be expected with AI Coding Assistants? – Future developments include more intuitive interfaces, adaptive learning to match developers’ styles, and enhanced capabilities for even greater productivity and creativity.
-
How can organizations gain a competitive advantage with AI Coding Assistants? – By strategically integrating tools like CodeBoost™, organizations can enhance efficiency, foster innovation, and deliver superior software solutions faster.
Generative AI (GenAI) technologies have emerged as a hallmark of innovation, promising to redefine the way we approach work in nearly every industry—software development more than most, as it radically shifts how we approach coding and problem-solving.
As leaders and decision-makers in enterprise software development, you’re likely no stranger to the allure of AI coding assistants. These tools, with their potential to automate tedious tasks, suggest code improvements, and even write substantial blocks of code, represent a significant leap forward. However, the journey from experimentation to realizing tangible, impactful results is fraught with challenges. Many organizations find themselves equipped with these powerful tools but unable to harness their full potential, leading to frustration and unmet expectations.
The excitement surrounding AI coding assistants is well-founded. Their ability to streamline workflows, enhance productivity, and foster innovation is undeniable. Yet, the key to unlocking these benefits lies not in the tools themselves but in how they are integrated and leveraged within your organization’s unique ecosystem. This is where a strategic, holistic approach becomes indispensable.
In this blog post, we’ll explore why a comprehensive strategy is crucial for effectively integrating GenAI into your software development processes. We’ll delve into how Cprime’s CodeBoost™, a pioneering solution that includes an AI coding assistant and many other powerful tools, exemplifies this approach by not only providing cutting-edge technology but also ensuring it is seamlessly woven into the fabric of your operations.
Join us as we uncover the path to transforming the promise of GenAI into a competitive advantage that propels your organization forward.
Unlocking the True Potential of AI Coding Assistants: Bridging the Gap Between Innovation and Impact
Despite the growing popularity of AI coding assistants in the realm of software development, a common narrative has emerged among enterprise leaders: the gap between the potential of these tools and the reality of their impact. This discrepancy isn’t due to a lack of innovation or capability within the tools themselves but rather a misalignment in their application and integration within existing workflows and strategic objectives.
AI coding assistants, by design, revolutionize how developers interact with code, offering unprecedented efficiencies in coding practices. They promise not just to automate the mundane but to elevate the quality of code and accelerate the development cycle. Yet, without a strategic framework that encompasses not only the adoption but also the integration and optimization of these tools, their full potential remains untapped.
The challenge, then, is not in finding the right AI coding assistant but in embedding it into the organizational fabric in a way that amplifies its strengths and aligns with broader business goals. This requires a shift from viewing these tools as standalone solutions to seeing them as integral components of a comprehensive development strategy. It’s about moving beyond the initial allure of automation and efficiency to a deeper understanding of how these tools can transform development practices, foster innovation, and drive competitive advantage.
Crafting a Strategic Blueprint for AI Coding Assistants in Software Development

The cornerstone of effectively leveraging AI coding assistants lies in a comprehensive strategy that extends beyond the initial adoption. This strategy should encompass:
- Custom solution development
- Seamless technological integration
- Thorough training for staff
- Ongoing support
Such an approach ensures not only the deployment of GenAI technologies but also their effective and sustained use, maximizing the return on investment.
Why out-of-the-box tools won’t suffice
Custom solution development is pivotal. Generic AI coding assistants, while powerful, cannot deliver their full value through a one-size-fits-all approach. Each organization has unique challenges, workflows, and goals.
Tailoring AI solutions to these specific needs ensures that the technology complements and enhances existing processes rather than disrupting them. An optimal solution will allow customization options that align with your team’s specific coding practices and project requirements, ensuring that the tool becomes a natural extension of your developers’ capabilities.
Integrating with your tool stack and workflows
Seamless technological integration is another critical element. An AI coding assistant should not stand apart from the tools and systems your team already uses but should integrate with them to create a cohesive and efficient workflow. This integration minimizes friction and learning curves, allowing teams to harness the benefits of AI more quickly and effectively, ensuring that the transition to using an AI coding assistant is as smooth as possible.
The need for training and support
Training and ongoing support are equally important. The introduction of AI into software development processes represents a significant shift in how tasks are approached and completed.
Comprehensive training ensures that your team can utilize the full range of capabilities offered by AI coding assistants, while ongoing support guarantees that any challenges encountered during implementation and use are promptly addressed. The best approach includes expert-led training sessions and on-demand coaching support, ensuring that your team is prepared to use your new tools, but also remains proficient over time.
By embracing this comprehensive strategy, organizations can unlock the full potential of AI coding assistants, transforming them from mere tools into catalysts for innovation, efficiency, and competitive advantage.
The Transformative Power of a Holistic AI Coding Assistant Solution
To appreciate the transformative potential of AI coding assistants, it’s crucial to understand the tangible benefits they bring to the table when integrated with a strategic, holistic approach. The impact of these tools extends far beyond mere efficiency gains. They become pivotal in driving innovation, enhancing code quality, and accelerating project timelines, ultimately contributing to a significant competitive advantage.
Innovation at the forefront
With AI coding assistants, developers are freed from the repetitive and time-consuming aspects of coding, allowing them to focus on creative problem-solving and innovation. This shift in focus fosters an environment where new ideas and approaches can flourish, directly impacting the organization’s ability to innovate and stay ahead in a competitive landscape.
Elevated code quality
One of the most significant advantages of integrating AI coding assistants is the substantial improvement in code quality. These tools are equipped with advanced algorithms that can suggest optimizations, identify potential errors before they become issues, and ensure adherence to best coding practices. The result is cleaner, more efficient, and more reliable code, reducing the time and resources spent on debugging and revisions.
Accelerated development cycles
The ability to generate code quickly and accurately has a direct impact on project timelines. AI coding assistants can dramatically reduce the time required to develop features, fix bugs, or implement changes, enabling teams to deliver projects faster without compromising on quality. This acceleration not only improves productivity but also enhances customer satisfaction by bringing products and updates to market more swiftly.
Strategic competitive advantage
The cumulative effect of fostering innovation, improving code quality, and accelerating development cycles is a significant competitive advantage. Organizations that effectively integrate AI coding assistants into their software development processes can achieve more with less, respond more rapidly to market changes, and deliver superior products and services.
By adopting a comprehensive strategy that includes optimally integrated AI coding assistants, organizations can not only optimize their development processes but also position themselves as leaders in the digital age.
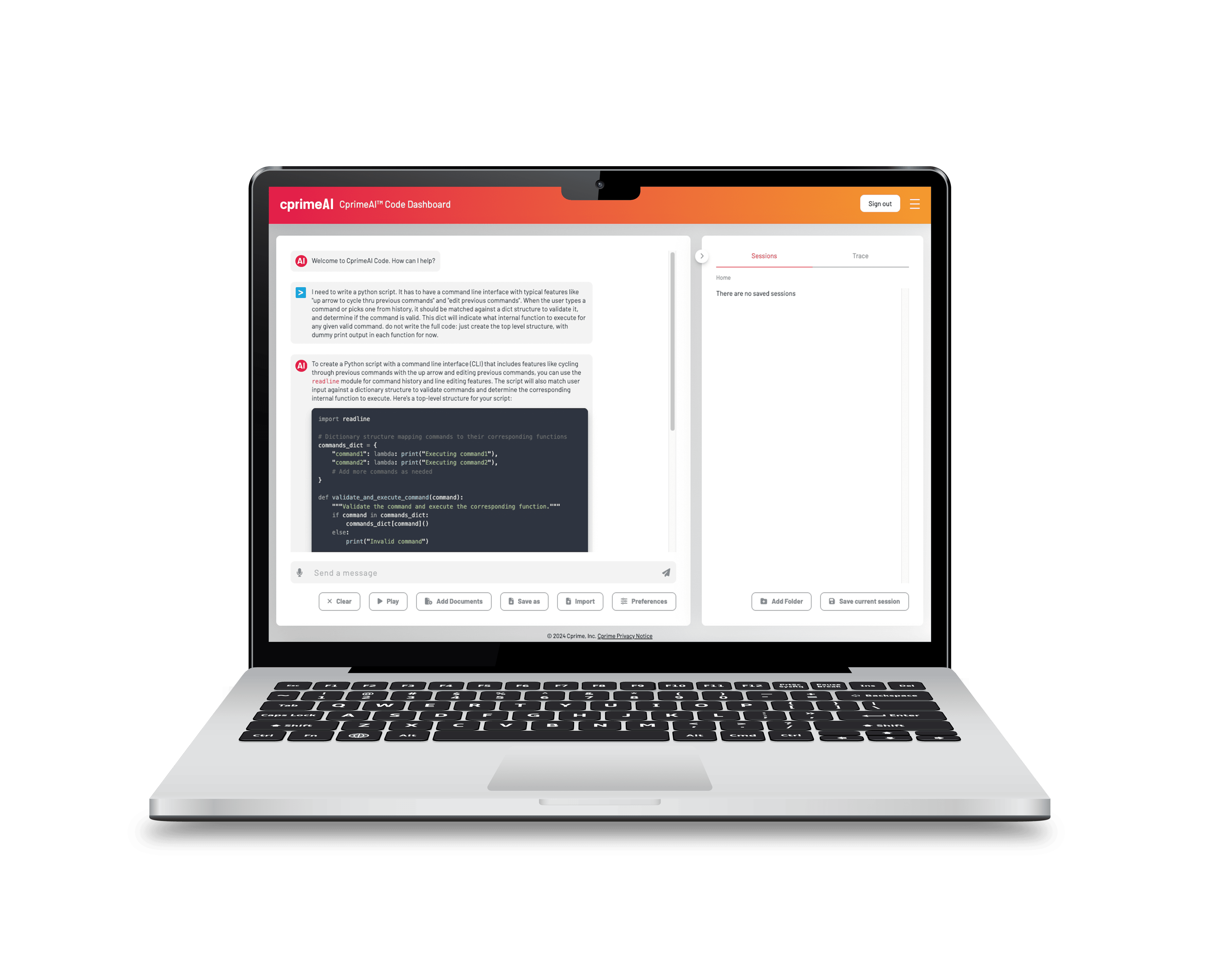
In embracing AI coding assistants within your software development lifecycle, it’s essential to partner with a provider that understands the intricacies of your development environment and offers a solution that aligns with your strategic goals. Cprime’s CodeBoost™ stands out as a prime example of such a partnership, offering a blend of cutting-edge technology, customization, and comprehensive support designed to seamlessly integrate with your operations and propel your projects forward.
Choosing the Right Partner for AI Integration
The journey towards integrating AI coding assistants should begin with selecting a partner that not only provides the technology but also understands the broader context of your development challenges and objectives. Cprime’s expertise in software development processes and its commitment to delivering tailored solutions make it an ideal partner for organizations looking to leverage AI for competitive advantage.
Customization and Flexibility
Every software development team has its unique set of practices, challenges, and goals. A one-size-fits-all AI tool may offer some benefits but will likely fall short of addressing specific needs. CodeBoost™ distinguishes itself by offering a level of customization and flexibility that ensures the tool not only fits into your existing workflows but also enhances them, driving efficiency and productivity.
Ongoing Support and Optimization
The integration of AI coding assistants into your development process is not a one-time event but an ongoing journey. As your projects evolve and new challenges arise, having access to expert support and continuous optimization of the tool becomes invaluable. Cprime’s commitment to ongoing support ensures that CodeBoost™ continues to meet your needs, helping you navigate the complexities of software development with ease.
A Strategic Approach to AI Integration
Ultimately, the successful integration of AI coding assistants like CodeBoost™ requires a strategic approach that goes beyond the technology itself. It involves understanding your development ecosystem, customizing the solution to fit your needs, and ensuring ongoing support and optimization. By partnering with Cprime, you’re not just adopting an AI tool; you’re embracing a comprehensive strategy designed to elevate your software development process and achieve tangible results.
In conclusion, the decision to integrate AI coding assistants into your software development lifecycle is a significant step towards enhancing productivity, code quality, and innovation. By choosing a partner like Cprime and leveraging solutions like CodeBoost™, you can ensure that this technology is not just an addition to your toolkit but a strategic asset that drives your organization forward in the competitive landscape of software development.
Choosing the Right Solution: The Strategic Advantage of CodeBoost™ (Powered by CprimeAI)
The journey from initial experimentation to achieving a transformative impact through these tools is complex, requiring a strategic approach that encompasses technology, process, and people. Cprime’s CodeBoost™ (powered by our proprietary private LLM platform, CprimeAI) exemplifies this journey, offering a glimpse into the future where AI and human creativity converge to redefine what’s possible in software development.
With solutions like CodeBoost™ leading the way, the future of software development is poised for a revolution, where AI and human ingenuity combine to create software solutions that are not only efficient and reliable but also innovative and impactful. The time to embrace this future is now, and the path forward is clear: a comprehensive, strategic approach to integrating AI coding assistants into your development processes.